Sap Business Objects Information Design Tool Tutorial
Creating a Semantic Layer with SAP Business Objects Universe
Describing SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence platform. They are built using the new Information Design Tool. A universe is an organized collection of metadata objectsthat enables business users to analyze and report on corporate data in non-technical language. For indepth understanding on SAP BO Tutorials click on: Information.
MOTIVATION
This material is an introduction to how to develop a SAP Business Objects Universe. It is aimed at students at universities, universities and other educational institutions with limited experience with Business Intelligence.
It can be used in the classroom or for self-study.
On completion of the course, students will be able to understand the basic concepts of a universe and how to design and develop a universe.
The material also serves as a reference for occasional users of SAP systems.
This version of the notes is designed for the SAP BOBJ Enterprise version
This version of the notes is designed for the SAP BOBJ Interactive Analysis trail version
LEARNING METHOD
The learning method used is “guided learning.” The benefit of this method is that knowledge is imparted quickly. Students also acquire practical skills and competencies. As with an exercise, this method explains a process or procedure in detail.
SAP Business Intelligence provides a broad range of reporting tools to facilitate decision making of the different end users. These tools can interact with data from different data sources. SAP Business Objects provides a semantic layer (universe) which facilitates the interaction with data sources and the extraction of data. This tutorial provided you with a step by step explanation of how to construct a universe which will be utilised in later reporting exercises.
Scenario
Global Bike International (GBI) is a world class bicycle company serving both professional and amateur cyclists. The company sells bicycles and accessories. In the touring bike category, GBI’s handcrafted bicycles have won numerous design awards and are sold in over 10 countries. GBI’s signature composite frames are world-renowned for their strength, low weight and easy maintenance. GBI bikes are consistently ridden in the Tour de France and other major international road races. GBI produces two models of their signature road bikes, a deluxe and professional model. The key difference between the two models is the type of wheels used, aluminium for the basic model and carbon composite for the professional model. GBI’s off-road bikes are also recognized as incredibly tough and easy to maintain. GBI off-road bikes are the preferred choice of world champion off road racers and have become synonymous with performance and strength in one of the most gruelling sports in the world. GBI produces two types of off-road bike, a men’s and women’s model. The basic difference between the two models is the smaller size and ergonomic shaping of the women’s frame.
GBI also sells an Accessories product line comprised of helmets, t-shirts and other riding accessories. GBI partners with only the highest quality suppliers of accessories which will help enhance riders’ performance and comfort while riding GBI bikes. Figure 1 displays the GBI range of products.
Traditionally GBI was a wholesaler who sold their bikes to retailers who then resold the bikes to the end consumers. Recently GBI has decided to sell their bike to the end consumer via the internet.
Organisational Structure
GBI’s headquarters are located in Dallas and the European subsidiary company (GBI Europe) is based in Heidelberg, Germany. In regards to the GBI sales process there are two sales organisations for America (Eastern US and Western US) and two for Germany (Northern Germany and Southern Germany). All sales organisations have a wholesale distribution channel responsible for delivering the products to the customers. However only one sales organisation is required in each country to support internet sales. The diagram below displays the GBI organisation to support the sales process.
Solution: First and foremost, please know that it is not necessary to know your computer id if you use Toontrack's Product manager authorization system.
Requirements
GBI management currently SAP ECC to manage and automate their business processes. They have discovered that one of their departments are using a Microsoft Access database to record sales data. The Department Heads have indicated that they would like the information provided in a user friendly format. This will facilitate them to gain greater insight to their sales data to understand the trends and sales performance. In response to these concerns, it was decided to build a number of reports using SAP Business Objects Interactive Analysis. To provide the connection between the data source (Microsoft Access) and the reporting tool a universe needs to be created.
SAP Business Objects Universe
What is a Semantic Layer?
A semantic layer is a business representation of corporate data that helps end users access data using common business terms.
Often when database developers build databases their main objectives involve the efficient creation, updating and deletion of data. They are not usually concerned about whether non database people understand the complexities of the underlying structures. While business users want to create reports based on the data contained in the database to facilitate decision making. The semantic layer insulates the business users from the underlying data complexity while ensuring the business is accessing the correct data sources and using consistent terminology.
The semantic layer enables users to use common business terms rather than the technical database language to access, manipulate, and organise information, it simplifies the complexity of the business data. The following diagram displays the various components of the semantic layer.
SAP Business Objects Universe
A Universe is a semantic layer tool used in Business Objects to map the data in your data source using everyday terms. The Universe enables the user to create a query to extract the data from a data source, describe it using common business terms and then analyse the data using different reporting tools. The Universe is used to run queries against the data source to extract data.
Below is an example of a Universe based on the GBI data.
The Universe structure contains:
-Connection details to a data source
-SQL structures (called Objects) to map the database structures (columns, tables, and database functions)
-A schema of the tables and joins used in the database
On the right of the screen is the schema of the database. While on the left are Universe objects that are required for reporting.
A Universe can be used to connect to a variety of data sources (Databases, Excel, XML, Text, Web Services.
The release of SAP Business Objects 4.0 provided functionality to connect directly with SAP solutions and thus a universe is no longer required to connect to SAP.
Building a Universe
You use the Business Objects Universe Designer (also referred to as Universe Design Tool) to create a Universe. However before you create a universe you need to create a database connection.
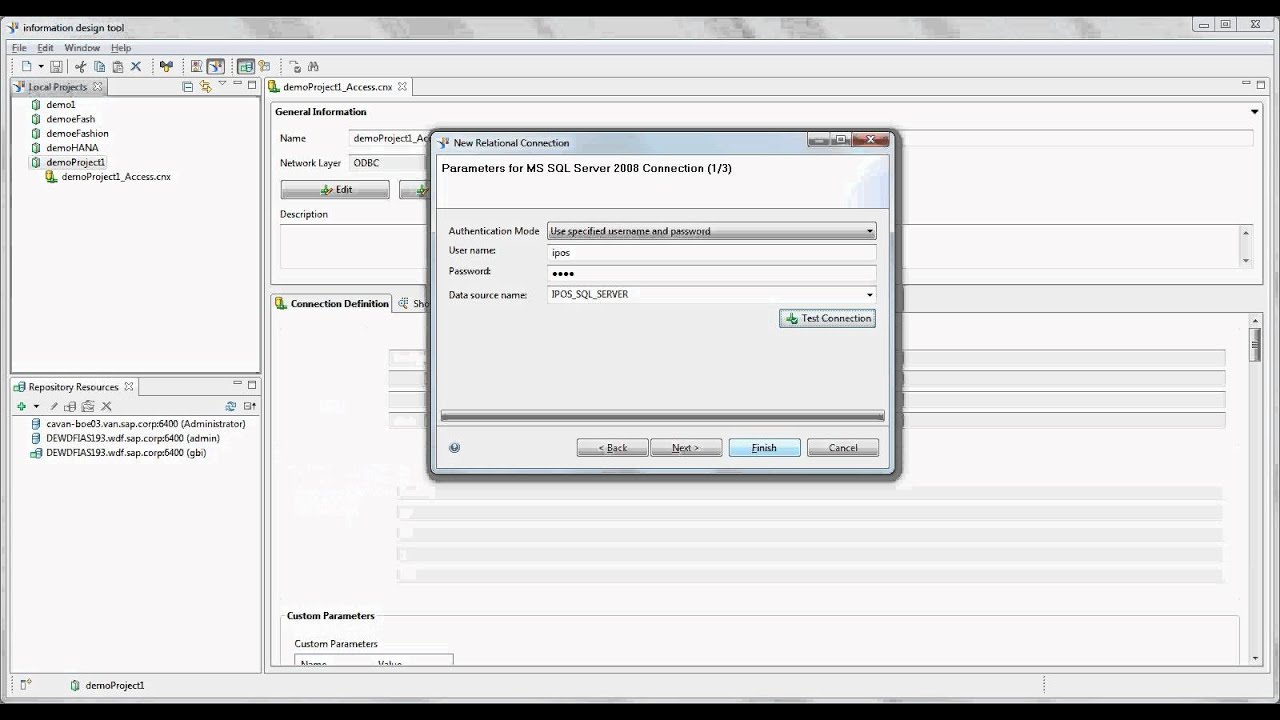
Creating a database connection
A data access driver is the software that connects the Universe to your middleware. Data access drivers provided with Business Objects include: IBM DB2, Informix, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, Sybase, Teradata, Hyperion, Generic OBDC.
For this exercise you are going to use OBDC connection drivers. OBDC (Open Database Connectivity) is Microsoft’s interface for accessing data in a heterogeneous environment of relational and non-relational databases.
You now need to select the appropriate driver for your data source. For this exercise you will be using a Microsoft Access database.
You will notice that your new Data Source connection is listed.
Creating a Universe
You create a Universe using the Universe Designer. To access the Universe Designer:
This wizard walks the user through the steps in creating a basic Universe. For the purpose of this exercise you will initially us the wizard. You can see that there are four steps in the process.
Step 1: Define the universe parameters
This step involves linking your new universe to the database connection you created previously.
The Database Middleware Selection screen appears.
- Type GBI Connection in the Connection Name field.
You will now need to select the OBDC driver for Microsoft Access 2007.
22. Scroll down till OBDC DriversMS Access 2007 appears
The following message should appear:
Step 2: Create Classes and Objects
A Universe uses classes and objects to represent the database’s structures. An object represents a column (data element), calculation or function in a data source. It represents a meaningful entity, fact, or calculation used in business environment. Objects are selected to construct a query. Once the query is performed, the objects are returned with values.
A class is a logical collection of objects. Most classes in Business Objects correspond to a table in the database. But this may not be user friendly for a business user.
The Create Initial Classes and Objects dialog screen lists the tables in the data source.
For indepth understanding click on
Goals
- This course is designed to give you the comprehensive skills needed to work with the Information Design Tool. The Information Design Tool enables designers to extract, define, and manipulate metadata from relational and OLAP sources to create and deploy SAP BusinessObjects universes.
- In this course you learn how to use data from different source systems (SAP and non-SAP) with the SAP BusinessObjects BI client tools.
Audience
- Application Consultant
- Data Consultant / Manager
- Database Administrator
- Developer
- Developer Consultant
- System Administrator
- System Architect
- Technology Consultant
Prerequisites
Essential
- Working knowledge of SQL and relational, also OLAP database management systems, concepts, and structures.
- OLAP database management concepts, systems and structures'
Recommended
- Basic knowledge of reporting with SAP BusinessObjects Web Intelligence or equivalent knowledge of how universes are used by the various SAP BusinessObjects analytics tools
Course based on software release
- SBOP BI Platform 4.2
Content
- Basic SAP BusinessObjects Universe Design
- Describing Universes
- Working with Local Projects
- Data Connections
- Defining Connections
- Data Foundations
- Creating Data Foundations
- Using Joins
- Business Layers
- Accessing Data through the Business Layer
- Integrating the Business Layer Components
- Validating Objects
- Creating Measure Objects
- Shared Projects
- Using Shared Projects
- Manipulating Other Designers' Resources
- Universe Deployment
- Deploying a Universe
- Loops in a Data Foundation
- Creating Loops on the Data Foundation
- Resolving Loops Using Aliases
- Resolving Recursive Loops
- Resolving Loops Using Contexts
- Data Restrictions
- Defining Data Restrictions
- Applying Mandatory Data Restrictions
- Applying Optional Data Restrictions
- Lists of Values (LOVs)
- Defining a List of Values
- Associating a List of Values to a Business Layer Object
- Parameters
- Creating and Using a Parameter
- Navigation Paths
- Defining and Creating Navigation Paths
- SQL Traps
- Defining SQL Traps
- Identifying a Chasm Trap
- Resolving a Chasm Trap
- Identifying a Fan Trap
- Resolving a Fan Trap
- Object @Functions
- Using @Functions in SQL
- Using the @AggregateAware function
- Using the @Select Function
- Using the @Where Function
- Using the @Execute Function
- Using the @Variable Function
- Extending the Data Foundation with Derived Tables and Calculated Columns
- Creating and Using Derived Tables
- Creating and Using Calculated Columns
- Universe Optimization
- Optimzing Universes
- Universe Management with Data Foundation and Business Layer Views
- Managing the Data Foundation Using Views
- Managing the Business Layer Using Views
- Universe Security
- Securing a Deployed Universe with Security Profiles
- Creating and Assigning Universe Security Profiles
- Identifying the Priority of Security Settings
- Updating a Deployed Universe
- Ambiguous Outer Join Resolution
- Resolving an Ambiguous Outer Join
- Universe Creation with Different Data Sources
- Identifying Different Data Sources
- Creating an OLAP Universe
- Creating a Universe from a BEx Query
- Creating a Multisource Universe
- Creating and Using Federated Tables
- Linked Universes
- Defining and Creating a Linked Universe
- Special Considerations of Linked Universes
- Managing Core Universes
- Prioritizing the Display of Tables Common to Multiple Core Data Foundations
- Including a Core Universe
- Universe Conversion
- Converting Existing .unv Universes
- Universe Translation
- Deploying a Universe in Different Lanugages
- Advanced Data Manipuliation in the Business Layer
- Using SQL to Manipulate Data
CPE Credits
040 CreditsPlease note CPE credits are available only for publicly scheduled courses delivered at SAP locations. CPE credits are not available for virtual classroom deliveries or customer specific deliveries.